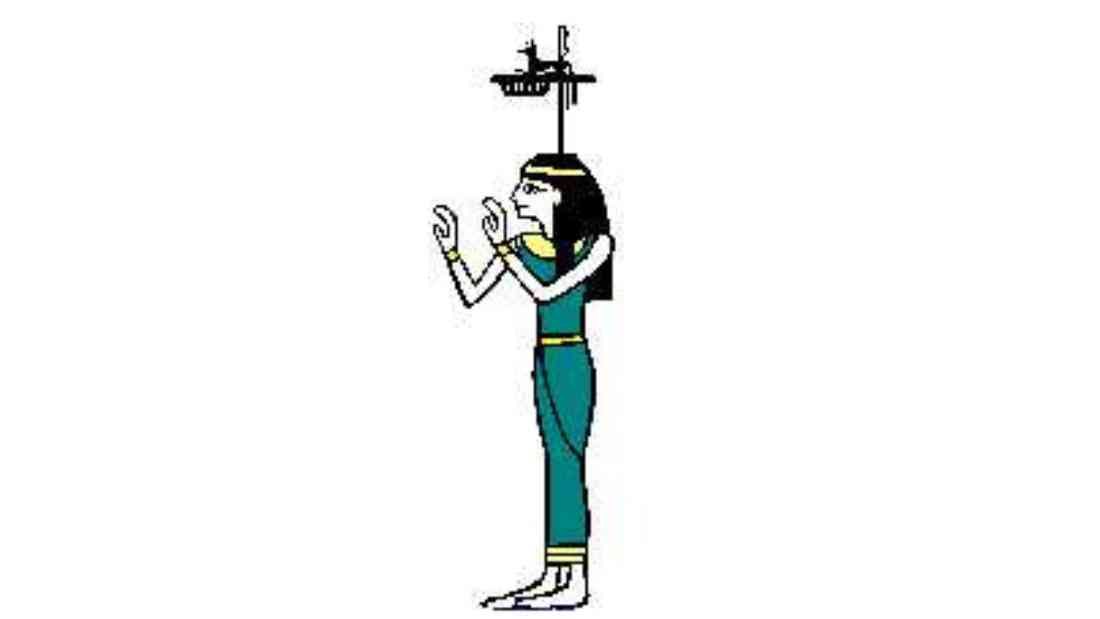
In ancient Egyptian mythology, Anubis is a well-known god associated with death, embalming, and the afterlife. However, what many may not be aware of is that Anubis also has a female counterpart, his wife, who is named Anput.
The Depiction of Anput, the Female Version of Anubis
The depiction of Anput in ancient Egyptian mythology is both captivating and significant.
Similar to Anubis, she is often depicted as a jackal-headed goddess, symbolizing her connection to death and the afterlife.
The jackal was an animal believed to possess keen senses, particularly in detecting the scent of decaying bodies.
This connection to death and its perception as a scavenger made the jackal an appropriate symbol for the guardianship of souls in the realm beyond.
In some cases Anput is depicted as a regal woman adorned in flowing garments and a majestic crown, exuding an air of grace and power.
As the devoted wife of Anubis, she shares in his divine responsibility as the guardian of the departed, guiding souls on their transcendent journey.
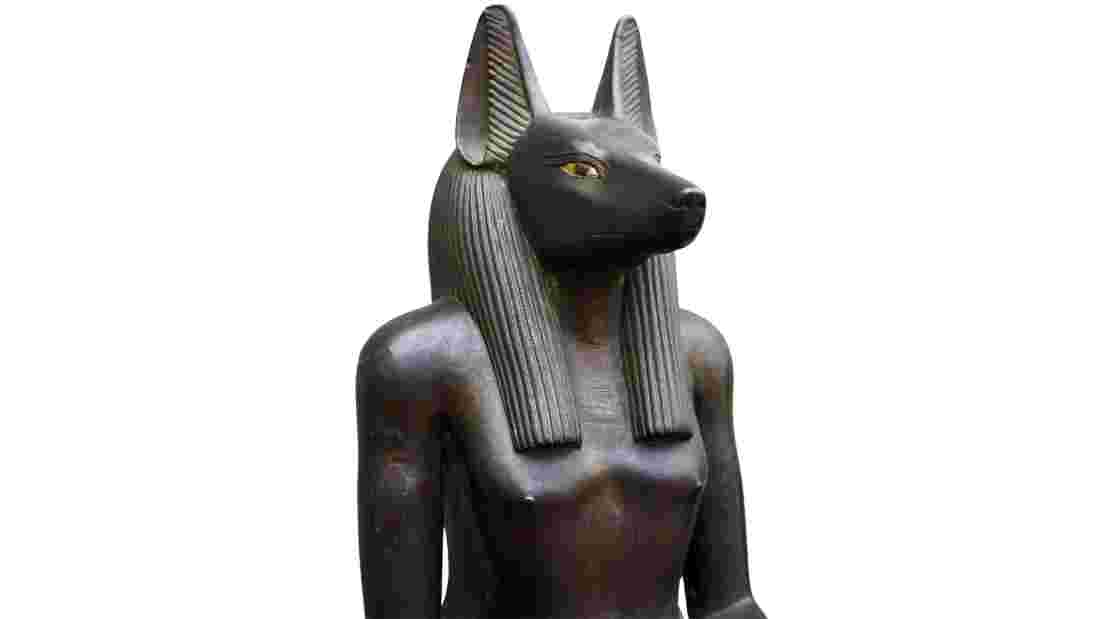

The Role of Anput, the Female Anubis
Anput played a significant role in the funerary rituals of ancient Egypt. She was believed to watch over the mummification process and protect the body of the deceased.
A Goddess of Mourning
Anput was also associated with the embalming process and was invoked to ensure the preservation of the body for the journey into the afterlife.
Anput’s presence is deeply intertwined with the somber rituals of mourning.
She oversees the sacred process of embalming and ensures the preservation of the deceased’s physical vessel for its passage into the afterlife.
Her watchful eyes observe every step, ensuring that nothing disrupts the sanctity of this intricate transformation.
A Protective Patroness
Beyond her association with death and mourning, Anput also assumes the role of a protective deity.
Invoked to shield the departed from malevolent forces, she acts as a spiritual safeguard during the perilous journey through the underworld.
Her divine essence fends off evil spirits, providing solace and reassurance to those making their passage.
She thus guides the soul of the deceased through the perilous journey of the underworld, ensuring their safe passage to the afterlife.
A Guiding Light
In the solemnity of funeral ceremonies and within the sacred confines of tombs, Anput and Anubis stand united.
Together, they guide the souls of the departed, illuminating their path through the labyrinthine realms of the afterlife.
With every step, Anput’s presence offers strength and guidance, ensuring a safe transition to the eternal realm.
Concluding Thoughts about Anput, the Wife and Female Version of Anubis
Anput, the female Anubis, is an embodiment of the duality found within Egyptian mythology.
Her portrayal as a guardian, protector, and guide reflects the ancient Egyptians’ profound reverence for the cycle of life, death, and rebirth.
Through her sacred duties, she helps to maintain the cosmic balance and honors the eternal legacy of those who have passed.

Frequently Asked Questions About Anput, the Wife and Female Version of Anubis
Anput is an ancient Egyptian goddess associated with mourning and protection. She is the wife and female version of Anubis, the god of embalming and the afterlife.
Anput played a significant role in funerary rituals. She was believed to watch over the mummification process, protect the body of the deceased, and guide their soul through the underworld to ensure a safe passage to the afterlife.
There is no substantial evidence of temples specifically dedicated to Anput. However, she was worshipped alongside other deities in various temples throughout ancient Egypt.
Anput is the female counterpart and wife of Anubis. While Anubis is primarily associated with embalming and the afterlife, Anput is specifically associated with mourning, protection, and the preservation of the deceased’s body.
Posts About the Egyptian Pantheon of Gods
The Pantheon of Ancient Egyptian Gods – A Comprehensive Guide
The Wrath of Montu – The Mythology of the Egyptian War God
Egyptian God Ammit – The Eater of Hearts in Ancient Egyptian Mythology
The Nightly Journey of Khonsu – The Ancient Egyptian God of the Moon
Ihy – The Joyful Ancient Egyptian God of Music
Min – The Ancient Egyptian God of Fertility
The Egyptian God Anubis – His Evolution from Son of Ra to Protector of the Dead
Unraveling the Mysteries of Babi – The Ancient Egyptian Baboon God
Ra, the Egyptian Sun God – Symbolism and Significance in Ancient Egyptian Culture
Sobek: The Ferocious Crocodile God of Ancient Egypt
The Enigmatic Mythology of Horus, the Egyptian Sky God
The Egyptian God Set – Protector of the Desert and Lord of Conflict
The Ancient Egyptian God Medjed: The Guardian of Osiris and the Afterlife
Anput, the Wife and Female Version of Anubis
Selket – The Scorpion Crowned Egyptian Goddess
Shu – The Egyptian God of Air, Wind, Peace and Lions
Hapi the Androgynous Ancient Egyptian God of the Nile
The Egyptian Sky Goddess Nut: Myth and Symbolism
The 42 Laws of Maat: The Moral Principles of the Ancient Egyptians
The Ancient Egyptian Goddess Mut: The Maternal Power in Egyptian Mythology
The Warrior Goddess: Neith in Ancient Egyptian Mythology
The God Bes: The Joyful Dwarf Deity in Ancient Egyptian Culture
The Egyptian Gods of Love: Hathor and Isis in Ancient Egyptian Mythology
Confronting the Serpent: The God Apep, the Nemesis of Ra in Egyptian Myth