Representation refers to how ideas, beliefs, values, and other aspects of different societies and cultures are imagined, expressed, shared, and understood by others, in both language-based or visual form.
This is considered ‘political’ because of considerations linked to who holds the power to create representations; whose voices are heard and amplified; which cultural practices are privileged or suppressed; and how the representations are interpreted and weaponised as a tool for domination or resistance, whatever the original intentions of the people who created the representation (Said 1973; Lockmann 2004).
When used in the context of post-colonial studies, the term “politics of representation” refers to how colonisers and colonised peoples were depicted and understood, as well as how their relationship was interpreted.

This includes examining power dynamics between the two groups, understanding the cultural and historical context for their interactions, and looking at how colonization still impacts present-day society.
Assessing the politics of representation makes it possible to better understand the complexities behind colonialism, imperialism, racialisation, and other dynamics that have shaped our contemporary world.
In this essay I will first address the issue of representation in anthropology, with a particular focus on the links between the discipline and colonialism, which led to much scholarly debate and criticism in the 1980s about potential bias in ethnographic and other scholarly representations of the colonised during the colonial era, which subsequently became the foundation for the emergence of post-colonial studies (Lockmann 2004).
I will then broaden the discussion to include other forms of representation, including the representation of power relations through discourse, photography and movies.

Anthropology is a representational discipline in which anthropologists seek to contextualize and interpret the complexities of the societies they study, representing their findings in the form of documentation, images, photos, artifacts, and stories kept in their archives or displayed in exhibitions and museums, scholarly papers and presentations made at conferences, as well as articles and books written for a general audience (Vargas-Cetina 2013).
It initially emerged as the study of the ‘primitive’ and the ‘exotic,’ with its origins firmly rooted in the power structures of the colonial era (Said 1973; Assad 1973; Lockmann 2004; Vargas-Cetina 2013; Gleach 2013).
Early anthropologists gained access to the subjects they were to study as part of the colonial apparatus, and while they may have tried to be neutral observers, it would be naïve to claim that their positionality, which hinged on the power inequalities in the relationship between coloniser and colonised, did not shape the outcomes of their research (Lockmann 2004).
This influence was one of the main thrusts of Said’s argument about the flawed representation of colonised nations by scholars representing the Orient –
‘… for a European or American studying the Orient there can be no disclaiming the main circumstances of his actuality: that he comes up against the Orient as a European or American first, as an individual second. And to be a European or an American in such a situation is by no means an inert fact’
Said 1973
(Said 1973, as cited in Lockmann 2004: 188).
Thus, anthropology came into being as the study by Europeans of non-European societies ruled by European powers, with the resulting representations meant for a European audience (Assad 1973: 90).
Beyond ethnographic representations created by early anthropologists, there were of course other forms of representation which shaped the Western public’s views of colonised peoples and cultures.
Artwork, literature, photography, cartoons and even human ‘zoos’ have been used to propagate ideas about ‘the Other’ that constructed a distorted vision of these societies while also reinforcing colonial power relations (Said 1973; Lockmann 2004; Vargas-Cetina 2013).
One of the seminal texts in the field is Edward Said’s Orientalism, which examines the politics of representation in the context of colonialism and imperialism in Eastern countries.
He argues that Western (European and American) perceptions of the East were shaped by a cycle of representation that presented “the Orient” as exotic, mysterious, and inferior.
The core premise perpetuated by the dichotomization of the East and the West, was the ‘othering’ of the East, based on preconceptions and attitudes that had little or no foundation.
In fact, many of the representations in question were often produced with little regard for or knowledge of the culture they were representing.
Through this process, he argues, colonised cultures were reduced to a set of stereotypes that explained and justified the inequality and oppression perpetuated upon them by Western powers (Said 1973; Lockmann 2004; Shohat & Stam 2014; Lutz and Collins 2020).

In the article ‘Shattered Myths,’ Said posits that much of the body of knowledge created by European and American scholars about ‘Arab society’ was in fact an exercise of ‘mythification,’ since ‘Arabs all told number over a hundred million people and at least a dozen different societies’ so it was impossible to study them ‘as a single monolith’ (Said 1975: 90).
He illustrates his point by referring to several examples of blinkered representations by Orientalists or Arabists (scholars who profess ‘to know the Arabs’ (Said 1975: 91)), focusing on articles written by Professor Gil Carl Alroy and Dr Harold Glidden as flagrant examples of the contentious ‘othering’ of non-Western cultures.
The former author makes several sweeping statements about Arabs, claiming that they are obsessed with violence and bloodshed and ‘psychologically incapable of peace,’ citing as proof of his claims various articles which appeared in Egyptian newspapers, ‘as if the two, Arabs and Egyptian newspapers, are but one’ (Said 1975: 90).

The latter, on the other hand, published an article in the American Journal of Psychiatry which purported to be a distilled psychological analysis of the Arab worldview, namely an obsession with revenge, the inability to be objective and make rational decisions, and the predilection for constant conflict, which were presented as the antithesis of Western ideals of peace and harmony (Said 1975: 91).
These two examples are not only reflective of a reductive view of Arab society, but are also highly political, since such representations can be, and in fact have been, used to legitimize and even encourage aggressive policies by Western powers, masking their aggression as an attempt to control or police the behaviour of people living in eastern countries.
The political implications of the abovementioned articles are very clear, but in other representations, such as those in photography and film, they can be covert, and one could argue, even more pernicious.
Through a careful selection of images and composition, photographers and filmmakers create narratives which have a powerful effect on how audiences understand and imagine the people and cultures being depicted (Shohat & Stam 2014; Lutz and Collins 2020).
The proliferation of photography and videography coincided with the heights of the imperial expansion projects of countries such as Britain, France and the United States.
Movies were much more accessible than literature or scholarly articles, creating new opportunities to craft representations of other cultures aimed for the consumption of the general public, including the illiterate (Shohat & Stam 2014).
When films were first introduced, audiences accepted what they saw on the big screen as fact, unaware of how filmmakers were manipulating the images and narratives to create different stories and portrayals.
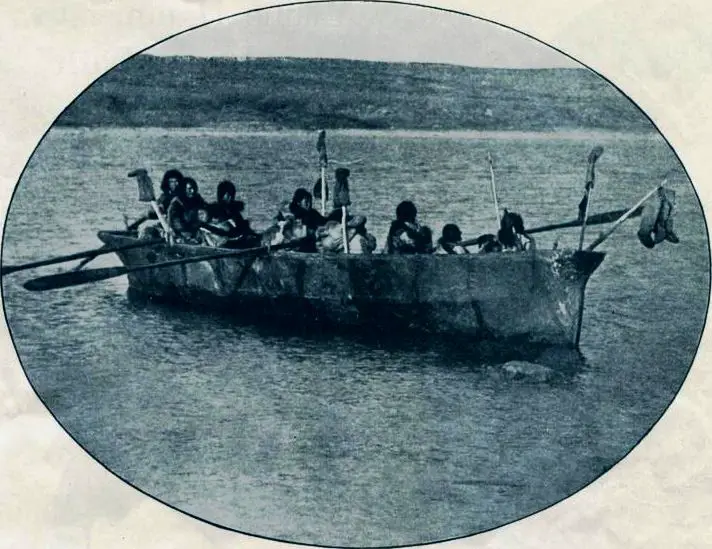
A case in point is Nanook of the North: A Story of Life and Love in the Actual Arctic, which was released by Robert Flaherty in 1922 and became a box-office hit.

The film was hailed as the first ‘documentary,’ but in truth it was fiction.
The characters in the film were actors, and the family that the camera supposedly followed unobtrusively for a year were simply acting a part.
Furthermore, by then the Inuit were using guns to hunt, but the movie showed them using old-fashioned harpoons.
Flaherty justified misrepresenting the lives that contemporary Inuit were living as an attempt to capture and ‘preserve’ on film the Inuit’s culture before it was tainted by modernity – however the audience who ended up watching the film accepted it as factual and a representation of the way the Inuit lived in 1922, and not a recreation of the ways of the past (Mackay 2017).

A similar phenomenon occurred when photographers and videographers travelled to far flung places in the empire.
The images and films they produced presented and ‘otherizing’ the alien cultures and landscapes as exotic and inferior to those of the West (Said 1973; Lockmann 2004; Vargas-Cetina 2013).
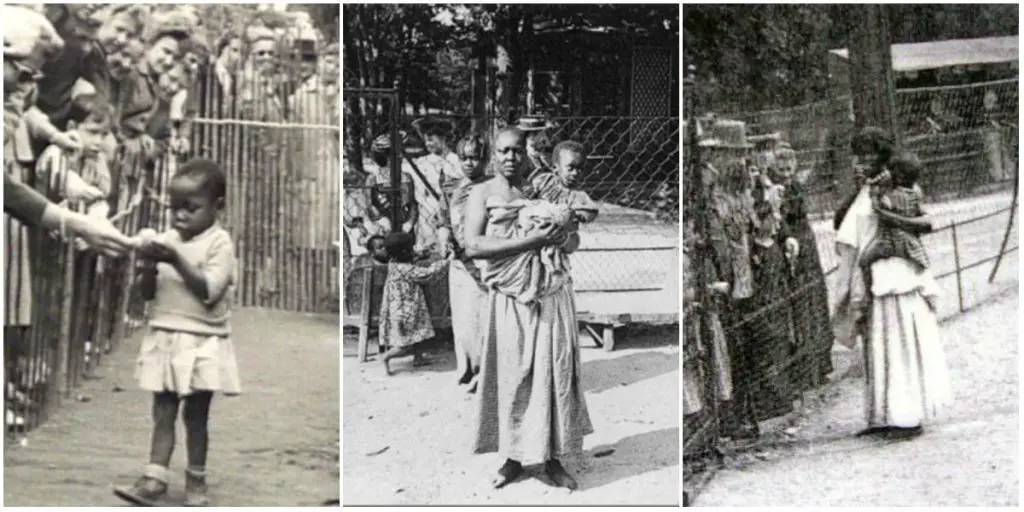
The natives were pictured as ‘primitive’ and infantilized, with videographers such as Martin and Ola Johnson, in the 1920s, portraying them as a form of wildlife, comparable to monkeys (Shohat & Stam 2014: 122).
This was by no means an accident, for the Western imagination was at the time enamoured of the Darwinian notion that Westerners were the apogee of the evolutionary process, while the natives discovered in the far-flung parts of the globe were inferior beings, much lower down on the evolutionary ladder.
This evolutionary perspective led to atrocities such as the caging of Ota Benga, an African Pygmy, at the Bronx Zoo, for the delectation of the American public; and the study of the anatomy of black people by zoologists, who compared them to mandrills and baboons (Shohat & Stam 2014: 122).
With time, videography ‘progressed’ from what was purported to be documentary or ‘fly-on-the-wall’ representations, to storytelling.
This gave film makers even more licence, and the result were movies in which Africans were presented as cannibals or the people of India portrayed as needing protection.
These storylines lent themselves well to the glorification of the colonisers as philanthropists committed to reforming or saving the savages. An excellent example is the 1937 film Wee Willie Winkie, where Colonel Williams explains to Shirley Temple that –
‘Beyond that pass, thousands of savages are waiting to sweep down and ravage India. It’s England’s duty, it’s my duty, to see that this doesn’t happen’
Colonel Williams (Shohat & Stam 2014: 126)

Lutz and Collins (2020) conducted an analysis of the photographs shown in National Geographic magazines between 1950 and 1986.
Their findings indicate that images were chosen to match an imaginary evolutionary scale based on skin colour, ranging from black / poor / strenuous physical labour / low technology / ethnic clothing / superstitious to white / wealthy / time for leisure / high technology machinery / western clothing / science.
Black people were thus portrayed engaged in strenuous physical labour, using simple tools and wearing ethnic clothing. They were also more likely to be shown conducting ‘exotic’ activities such as ritual dances.
People with bronze skin tones, on the other hand, were portrayed as less poor than those who were black and using tools that were slightly more advanced.

And finally, at the other end of the scale, white people were portrayed using state-of-the-art machinery, wearing western clothes and the trappings of wealth, and in several cases at leisure (Lutz and Collins 2020: 97-100).
The authors concluded that the selection of images sent a subliminal message to readers that ‘at one point people of color were poor, dirty, technologically backward and superstitious – and some still are. … [but] With guidance and support from the West, they can in fact overcome these problems, acquire the characteristics of civilized peoples, and take their place alongside them in the world’ (Lutz and Collins 2020: 99).
What better way of justifying Euro-American exploitation of African and Asian countries than by deploying a narrative that black and bronze people were ‘poor’ and ‘backward’ and that the Western forays into their countries would help them to modernize and improve their quality of life?
The politics of representation is thus a very important part of post-colonial studies because it examines how certain images, words and stories were used to represent non-western peoples, creating over-generalisations based on an ethnocentric cultural hierarchy of differences and values, acting as justification and camouflage for the exploitation and subjugation of the ‘Other’ in the name of progress.
Bibliography
Asad, T. (1979) ‘Anthropology and the Colonial Encounter.’ In Huizer, G., Mannheim, B. (eds), The Politics of Anthropology: From Colonialism and Sexism Toward a View from Below. De Gruyter, Inc., Berlin/Boston.
Gleach, F. (2013) ‘Notes on the Use and Abuse of Cultural Knowledge.’ In Vargas-Cetina, G, Nash, J., Igor Ayora-Diaz, S., Conklin, B.A. and Field, L.W. (eds), Anthropology and the Politics of Representation. The University of Alabama Press: Tuscaloosa, pp. 176–190.
Lockman, Z. (2004) ‘Said’s Orientalism: A Book and Its Aftermath.’ Contending Visions of the Middle East. Cambridge University Press, pp. 182–214.
Lutz, C., and Collins, J. (2002) ‘The Color of Sex: Postwar Photographic Histories of Race and Gender.’ In Askew, K., Wilk, R. (eds), The Anthropology of Media. Blackwell Publishers, Oxford.
Said, E. (1975) ‘Shattered Myths.’ In Naseer, H. (ed.), Middle East Crucible. Medina University Press, pp. 410 – 427.
Shohat, E., Stam, R. (2014) Unthinking Eurocentrism: Multiculturalism and the Media (2nd ed.). Routledge, London.
Mackay, R. (2017) ‘Nanook of the North: All the Worlds a Stage.’ Queen’s Quarterly, vol. 124, no. 2, pp. 249–258.
Vargas-Cetina, G. (2013) ‘Introduction: Anthropology and the Politics of Representation.’ In Vargas-Cetina, G, Nash, J., Igor Ayora-Diaz, S., Conklin, B.A. and Field, L.W. (eds) Anthropology and the Politics of Representation. The University of Alabama Press, Tuscaloosa, pp. 1–15.
For Further Reading
What are the key components of the anthropological perspective?
“Cultural values are a web of linked concepts, fixed in time and space.”
Evans-Pritchard and the Religion of the Nuer Tribe
How do economic and residence practices impact women’s status and power?
What are the different marriage wealth-exchange practices?
Claude Lévi-Strauss’s Structuralism and its Influence on Anthropological Thought
Clifford Geertz and the Thick Description of the Balinese Cockfight
Bronislaw Malinowski, the Trobriand people and the Kula
Dance as Ritual – an anthropological perspective
How Residence Customs After Marriage Vary Around the World
Compare the operations and implications of Bridewealth and Dowry
The impact of Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ARTs) on Anthropology
“The two-gender system is neither innate nor universal” (Towle and Morgan 2006)
The 4 Main Branches of Anthropology – Unlocking the Secrets of Human Diversity
Anthropology vs Sociology – Which Lens to Use When Studying Humanity?

